The multi-source fused road information-driving comfort dataset
is designed to predict the driving comfort of autonomous vehicles
by leveraging road-related data.
Our application in the Nature Communications:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57845-z
Multi-source
heterogeneous data fusion
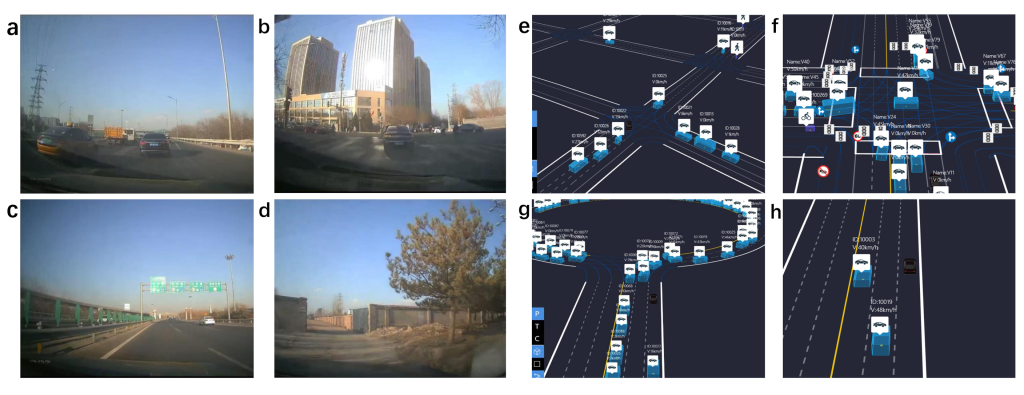
The dataset integrates real vehicle dynamic data (274 groups) and high-fidelity simulation data (252 groups), covering four types of typical driving scenarios (urban expressway, urban road, highway, rural road) and four types of microscopic road conditions (straight road, intersection, circle island, traffic emergency).
Multi-dimensional
road feature system
The three-level feature structure covers macroscopic road network features (total path length, average speed, traffic congestion index, weather coding), meso-segment features (signal density, intersection topology complexity, curvature radius of curve) and microscopic dynamic features (traffic emergency frequency, pedestrian/bicycle penetration probability, lane number gradient).
Multi-modal
comfort index
The objective measurement and subjective evaluation are combined to form a scientific quantitative system. The human-vehicle-road collaborative quantification is realized, which provides an interpretable objective function for path planning.
Set Up
Real vehicle data acquisition
Data acquisition platform
- Vehicle: Equipped with Dewesoft SIRIUS XHS data acquisition system, DS-IMU inertial measurement unit, GPS antenna.
- Personnel: There must be at least one driver and one safety officer.
Collecting content
- Dynamic parameters:
- Longitudinal/lateral acceleration (ax,ay), plus acceleration (jerk), velocity, heading Angle.
- Road information:
- Real-time traffic congestion index, number of signal lights, and intersection density are obtained through the map API.
- Environment parameters:
- Weather (sunny/rainy/snowy), light conditions.
Simulation data generation
Simulation tool
- 51sim-one autonomous driving simulation platform.
Configuration parameters
- Traffic flow:
- Vehicle type (car: bus: engineering vehicle =7:2:1), pedestrian/bicycle density.
- Road conditions:
- Road surface roughness (mapped by road level), curve radius, slope.
- Dynamic events:
- Preset emergency braking, lane cutting, pedestrian avoidance and other scenarios.